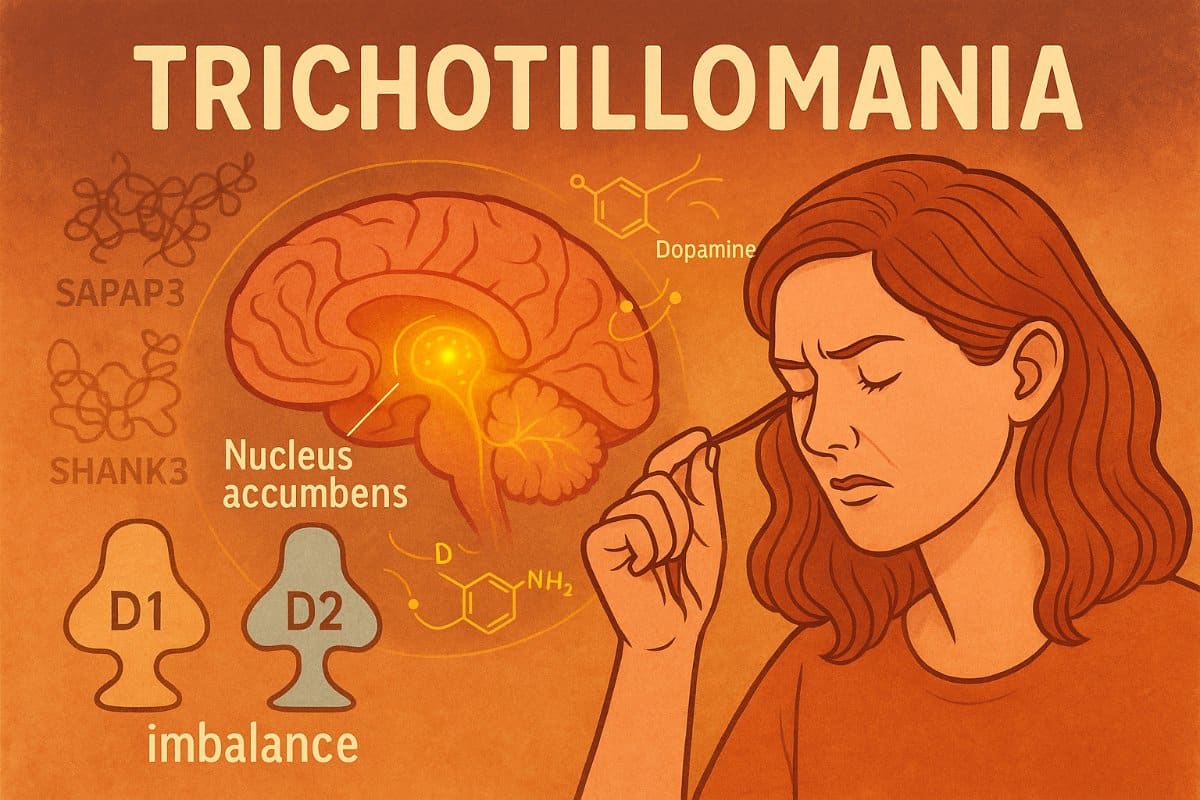
Summary: A new study using SAPAP3 knockout mice sheds light on the brain mechanisms that may drive trichotillomania, or hair-pulling disorder. These mice displayed compulsive grooming, heightened aggression, and stress-sensitive behaviors, mirroring human TTM traits—particularly in females. Neural recordings revealed reduced nucleus accumbens activity alongside dopamine receptor imbalances and altered synaptic protein interactions. The findings suggest that targeting reward circuit …
Read More »