The breakup of the ancient supercontinent Nuna during Earth’s “Boring Billion” years drastically shook up the planet, and the reshuffle may have created the conditions that gave rise to complex life, new research shows in unprecedented detail. The Boring Billion refers to the period between 1.8 billion and 800 million years ago. Even though this interval encompassed the breakup and …
Read More »Tag Archives: supercontinent
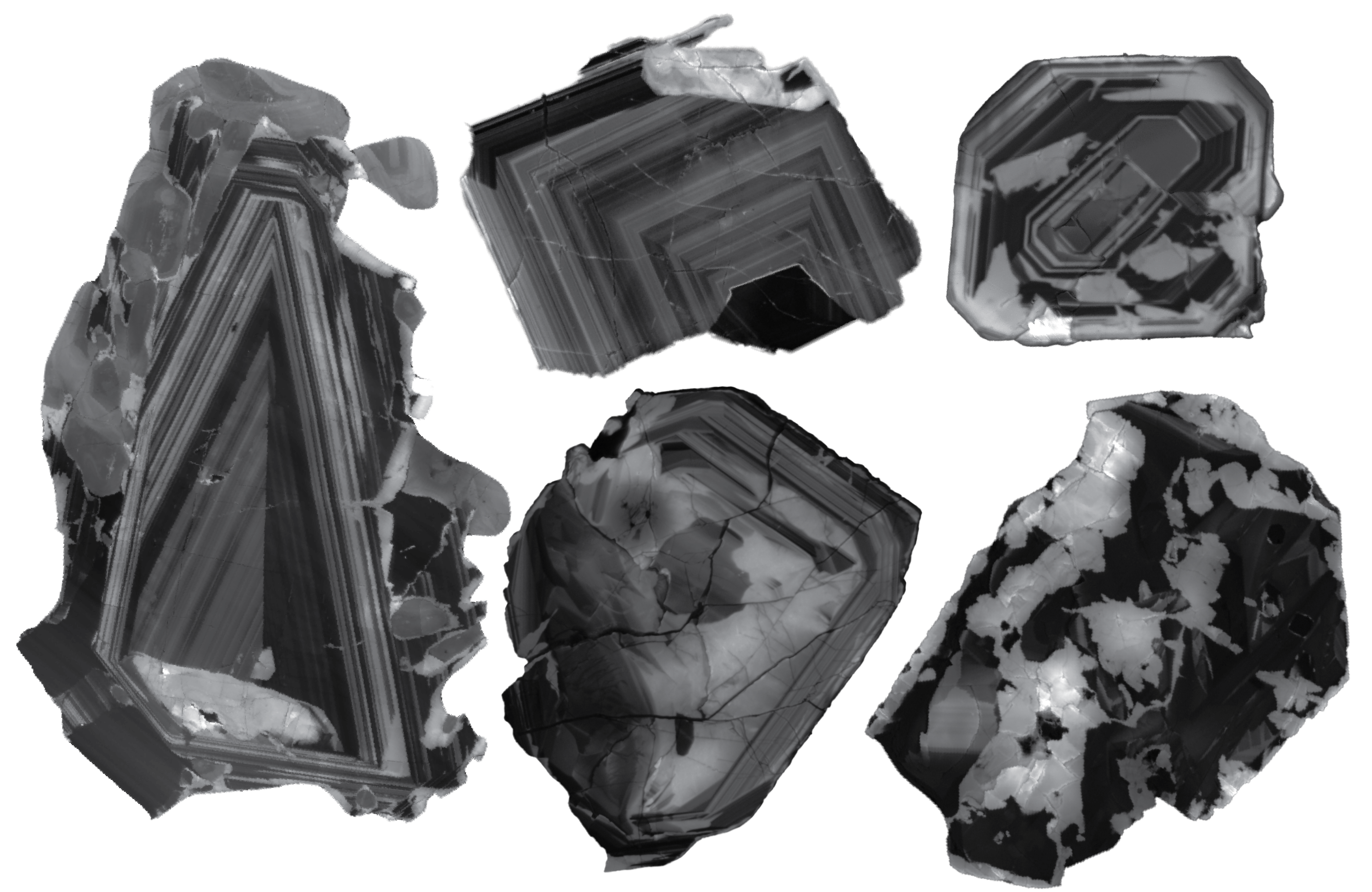
Vast source of rare Earth metal niobium was dragged to the surface when a supercontinent tore apart
A recently discovered enormous source of niobium — a metal that’s essential for much of today’s technology — appears to have formed when the supercontinent Rodinia ripped apart around 830 million years ago, according to a new study. The niobium-rich carbonatites, which could be one of the world’s largest sources of the metal, have come from deep within the Earth’s …
Read More »Lake Superior rocks reveal build up to giant collision that formed supercontinent Rodinia
Around 1.1 billion years ago, the oldest and most tectonically stable part of North America — called Laurentia — was rapidly heading south toward the equator. Laurentia eventually slammed into Earth’s other landmasses during the Grenville orogeny to form the supercontinent Rodinia. Laurentia’s path during that period is known, thanks to paleomagnetism. By tracing the orientation and magnetism of rocks …
Read More »