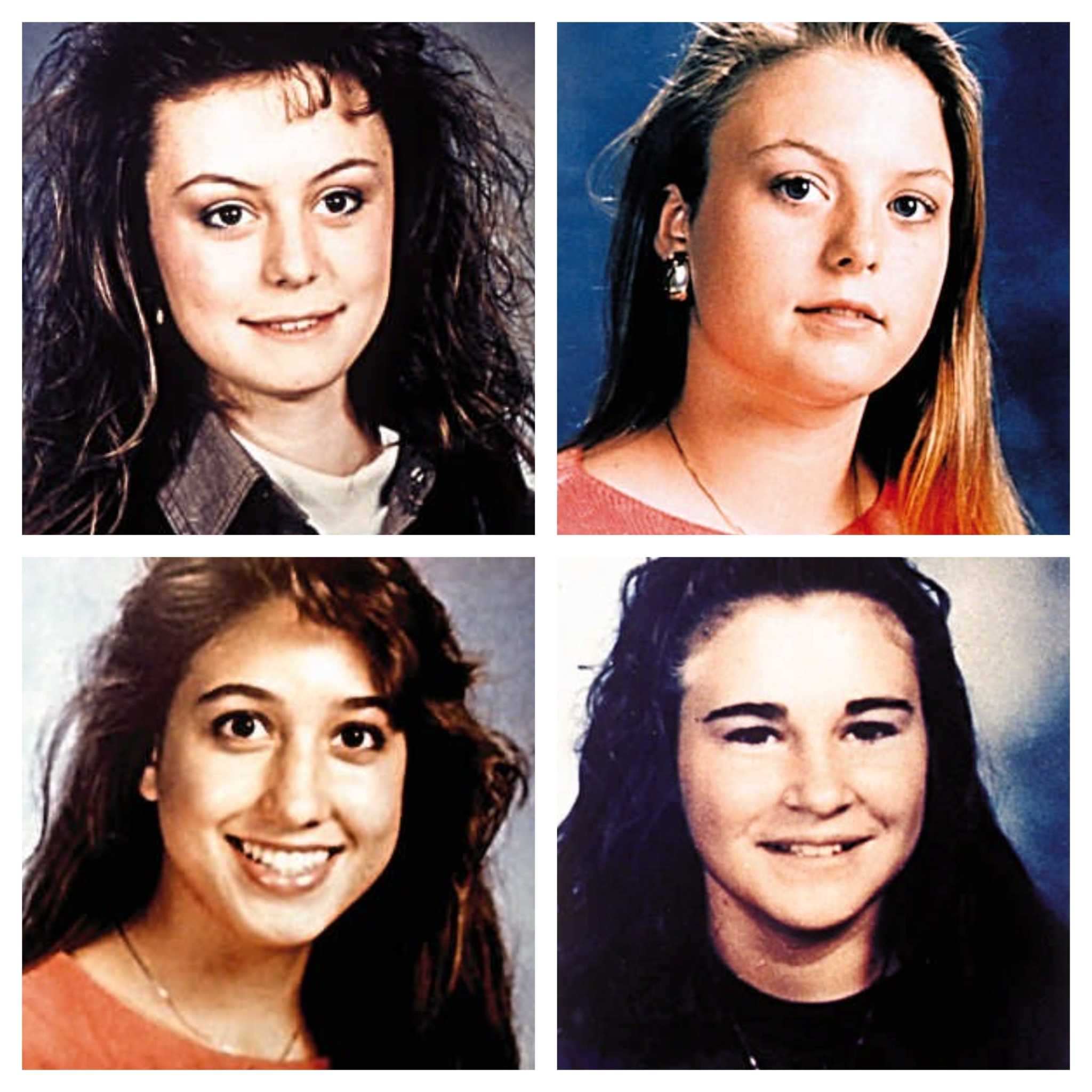DNA can store information for millions of years without any energy input, but scientists have lacked reliable energy sources to enable DNA computations. Credit: Kateryna Kon/SPL Researchers have found a new way to power DNA computers — tiny biological devices that perform calculations using biochemical properties of DNA bases rather than conventional silicone chips, which use electricity to carry out …
Read More »Tag Archives: DNA
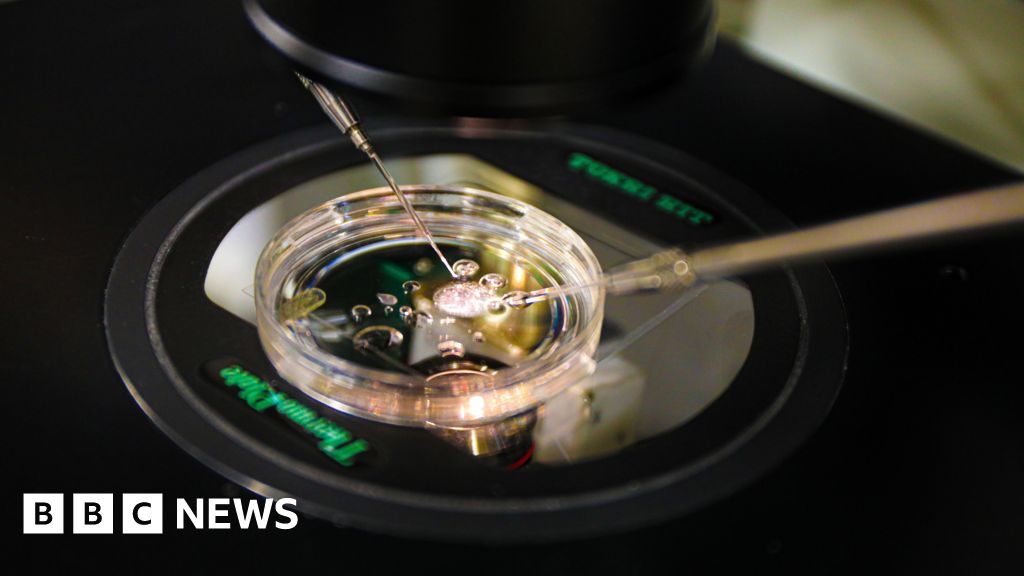
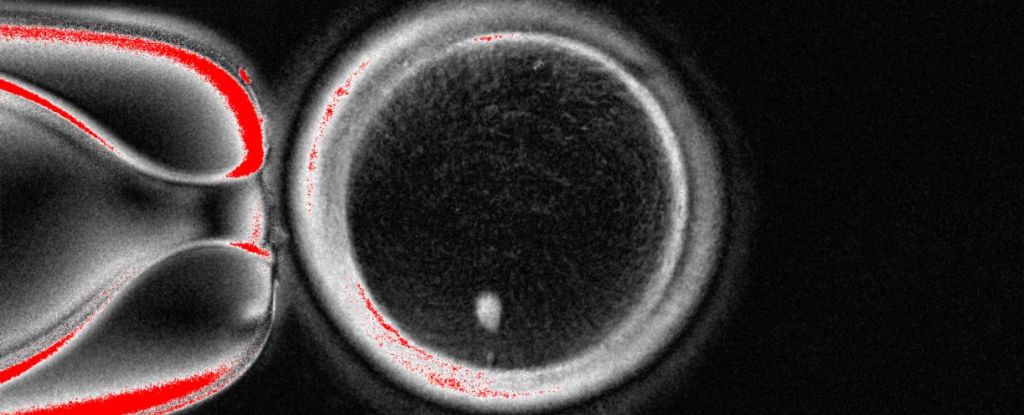
Working Egg Cells Made Using DNA From Human Skin in World First : ScienceAlert
Scientists have created egg-like cells capable of fertilization using DNA from ordinary skin cells in what could be a major breakthrough for infertility research. Using a newly developed technique to remove excess chromosomes, a team led by clinical biologist Nuria Marti-Gutierrez of Oregon Health & Science University has created human eggs that can undergo successful fertilization and start to develop …
Read More »Human skin DNA fertilised to make embryo for first time
James GallagherHealth and science correspondent OHSU/Christine Torres Hicks US scientists have, for the first time, made early-stage human embryos by manipulating DNA taken from people’s skin cells and then fertilising it with sperm. The technique could overcome infertility due to old age or disease, by using almost any cell in the body as the starting point for life. It could …
Read More »Miscarriages, down syndrome, and infertility all linked to this hidden DNA process
When a woman becomes pregnant, the outcome of that pregnancy depends on many things — including a crucial event that happened while she was still growing inside her own mother’s womb. It depends on the quality of the egg cells that were already forming inside her fetal ovaries. The DNA-containing chromosomes in those cells must be cut, spliced and sorted …
Read More »Shell Casings and DNA on Fingernails Helped Crack ‘Yogurt Shop’ Murder Case – The New York Times
Shell Casings and DNA on Fingernails Helped Crack ‘Yogurt Shop’ Murder Case The New York Times New details: How Austin Police identified yogurt shop murders suspect KUT Austin police confirm 1991 yogurt shop suspect passed through El Paso post-murders KFOX Detective’s shirt brings closure to families of yogurt shop murder victims Austin American-Statesman DNA helps solve ‘haunting’ yogurt shop quadruple killings more than 3 …
Read More »How long does DNA last?
Scientists have been using ancient DNA to investigate questions about extinct animals since 1984, when researchers recovered two pieces of DNA from a museum specimen of a quagga, a zebra-like species that went extinct in the 19th century. Over the past 40 years, advancements in technology have allowed scientists to sequence older and older DNA from animals and plants, with …
Read More »Tyler Robinson: The evidence so far against the Charlie Kirk shooting suspect, confessions, DNA and his grandfather’s rifle
More than two weeks after Charlie Kirk, the conservative firebrand and close ally of President Donald Trump, was shot and killed while speaking at Utah Valley University, his suspected killer is set to appear in court Monday – the next step on the lengthy road to a state trial. Tyler Robinson, a 22-year-old who grew up in a Utah suburb …
Read More »Yogurt Shop Murders Solved After 34 Years Thanks To DNA Testing
Investigators believe they finally have solved the infamous and gruesome 1991 killings of four teenage girls inside an Austin frozen yogurt shop, known as “The Yogurt Shop Murders,” after 34 years. On Friday, the Austin Police Department announced that it has identified suspect as Robert Eugene Brashers through “a wide range of DNA testing.” Brashers, who has been linked to …
Read More »Austin’s Yogurt shop murders solved 34 years later with DNA testing
Authorities investigating the 1991 murders of four teenage girls at a North Austin “I Can’t Believe It’s Yogurt” shop believe they have solved the case through newly available DNA testing, closing the chapter on one of the city’s darkest crimes, the American-Statesman has learned. Top Austin police leaders and cold case detectives plan to announce Monday that they have linked the …
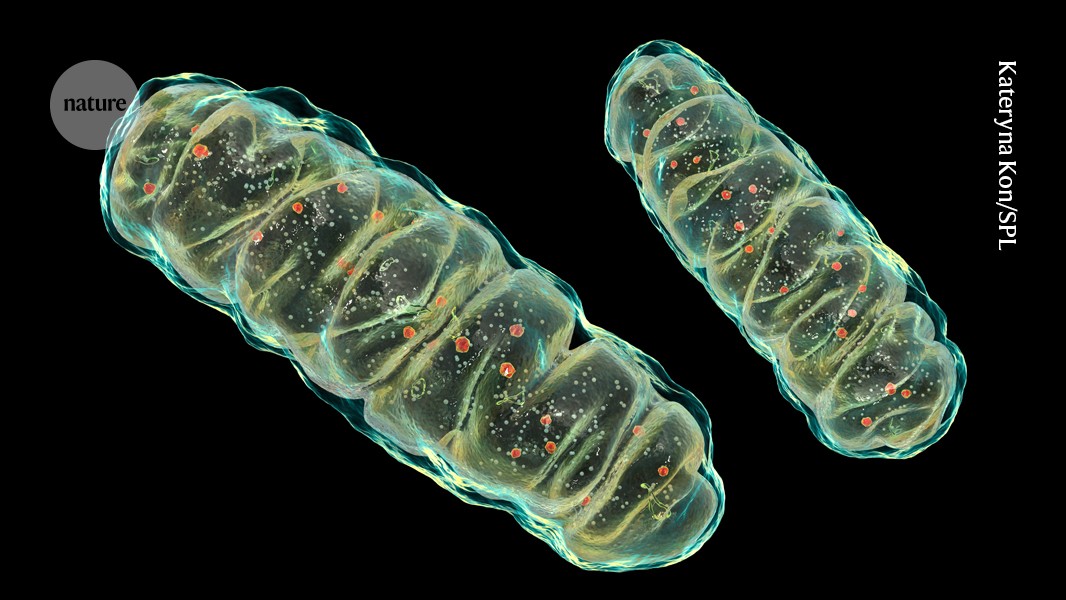
Read More »Mitochondria expel tainted DNA — spurring age-related inflammation
Mitochondria (illustration) have their own DNA, which they expel into their environment if the molecules don’t meet their standards.Credit: Kateryna Kon/Science Photo Library The cellular batteries known as mitochondria sometimes dump DNA into their surroundings, which can contribute to inflammation during ageing. Now a study in mice reveals why this dumping occurs: mitochondria are expelling ‘tainted’ DNA1. Scientists found that, …
Read More »