Pieces of bacteria migrating from the gut to the brain may play a key role in sleep, scientists have discovered, suggesting that the oldest and most basic microorganisms in our bodies are crucial in telling us when to nod off. These fragments are made of a chemical called peptidoglycan, which comes from bacterial cell walls in the digestive system. Previous …
Read More »Tag Archives: Brains
Drugs Like Ozempic Quieten ‘Food Noise,’ in Our Brains, Study Finds : ScienceAlert
Obsessive, intrusive thoughts about eating – known as food noise – can be quieted through semaglutide drugs such as Ozempic, new research has revealed, further boosting the effectiveness of these treatments for weight loss. These drugs are known as receptor agonists, triggering cell responses to mimic the body’s natural glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) hormone, and reduce appetite and slow digestion. We …
Read More »Fat fuels our brains in new AIBN discovery – Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology
New research from the Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (AIBN) has revealed that neurons in the brain use fats for energy, challenging decades of scientific thinking and opening the door to new treatments for neurological disease. For years, scientists believed that healthy neurons, the brain’s communication cells, relied solely on glucose and its metabolites to power their activity. But …
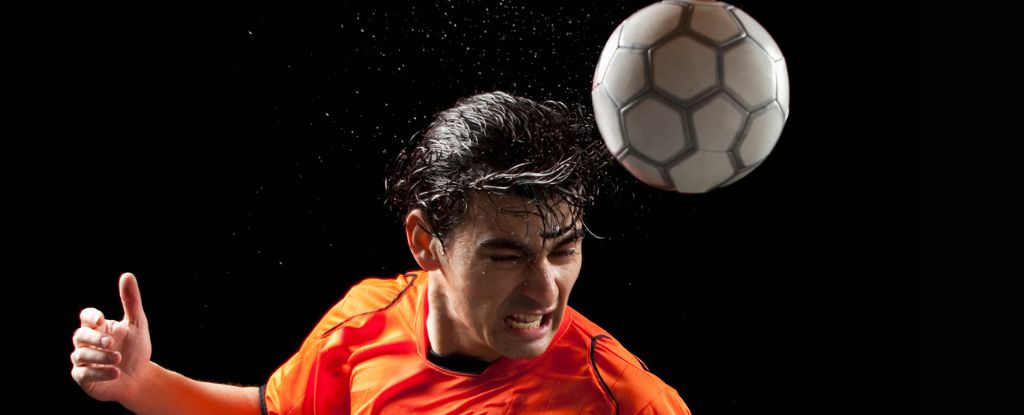
Read More »Soccer Headers Damage Brains Even Without Concussions, Large Study Finds : ScienceAlert
The world’s most popular sport is reckoning with serious health concerns. The largest study of its kind has now found that repetitively heading a soccer ball can negatively impact the brain, even in amateur players who don’t report concussions. Among 352 amateur adult soccer players, those who took more than a thousand headers a year showed microscopic changes to the …
Read More »Scientists pinpoint the brain’s internal mileage clock
Victoria GillScience correspondent, BBC News Getty Images Scientists have for the first time located the “mileage clock” inside a brain – by recording the brain activity of running rats. Letting them loose inside a small, rat-sized arena, the researchers recorded from a part of their brains that is known to be important in navigation and memory. They found that cells …
Read More »Just 4 Days of Junk Food Can Rewire Your Brain’s Memory Center
Scientists have discovered that junk food can alter brain memory circuits within days. The research hints that early lifestyle interventions might help safeguard memory and prevent long-term cognitive decline. Credit: Stock A high-fat diet quickly disrupts neurons tied to memory, but restoring glucose or dietary changes can repair the damage. These findings may guide strategies to reduce dementia risk. Diet …
Read More »different people’s brains process colours in the same way
Our brains seem to respond to specific colours in a similar way. Credit: Hispanolistic/Getty Is the colour you see the same as what I see? It’s a question that has puzzled both philosophers and neuroscientists for decades, but has proved notoriously difficult to answer. Now, a study that recorded patterns of brain activity in 15 participants suggests that colours are …
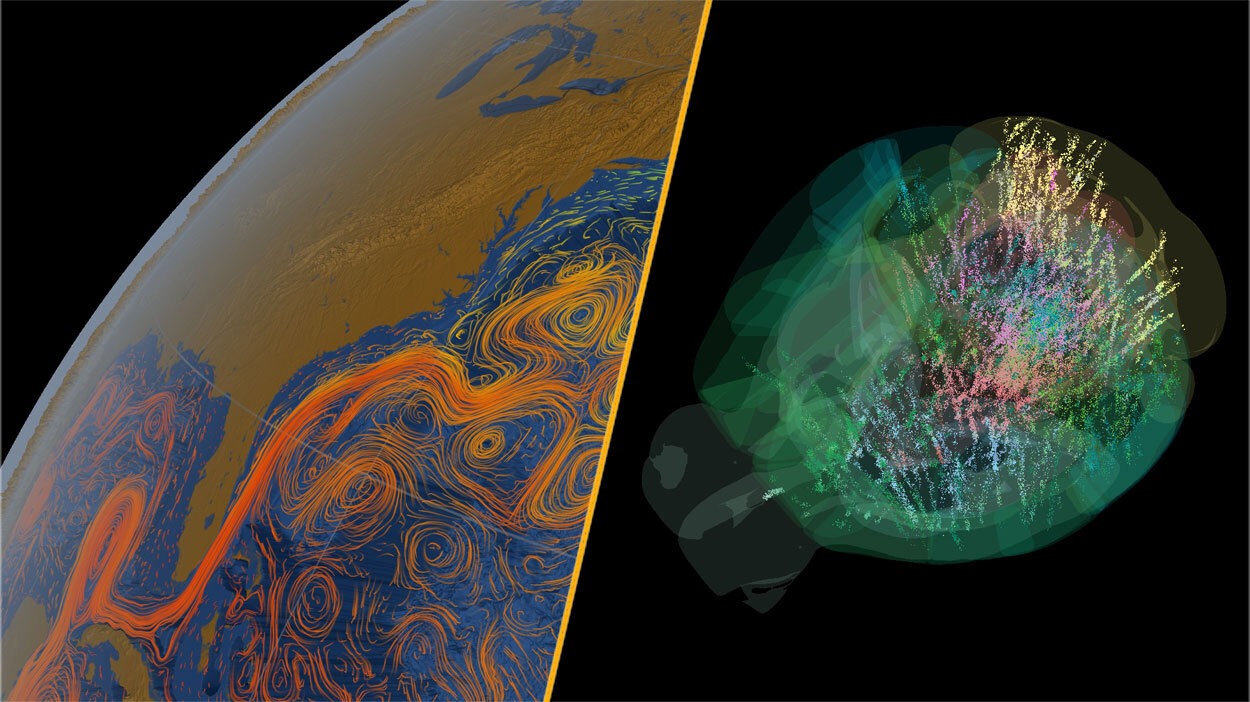
Read More »Science news this week: A key Atlantic current nears collapse, the world’s biggest iceberg shatters, and mouse brains rewrite neuroscience
The watery part of the world dominated our science news coverage this week, beginning with the alarming prediction that a key Atlantic current, the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which includes the Gulf Stream, could begin its irreversible collapse in decades. That’s according to a new landmark study, which combined the predictions of 25 climate models to arrive at an …
Read More »Autism Gene Found to Alter Brain’s Social Hormone Signals
Summary: A new study reveals how a mutation in the Shank3 gene, associated with autism, alters social behavior by disrupting vasopressin release in the brain. In mice, this mutation reduced sociability and defensive aggression by limiting vasopressin reaching the lateral septum. Researchers showed that vasopressin acts through two distinct receptors: AVPR1a for sociability and AVPR1b for aggression. By selectively targeting …
Read More »3 Psychiatric Tools That Could Boost the Brain’s Natural Healing – The New York Times
3 Psychiatric Tools That Could Boost the Brain’s Natural Healing The New York Times Source link
Read More »