Intel says that systems with these chips in them should be shipping by the end of the year. In recent years, the company has launched a small handful of ultraportable-focused CPUs at the end of the year, and then followed that up with a more fully fleshed-out midrange and high-end lineup at CES in January—we’d expect Intel to stick to that basic approach here.
Panther Lake draws near

Intel
Panther Lake tries to combine different aspects of the last-generation Lunar Lake and Arrow Lake chips.
Intel
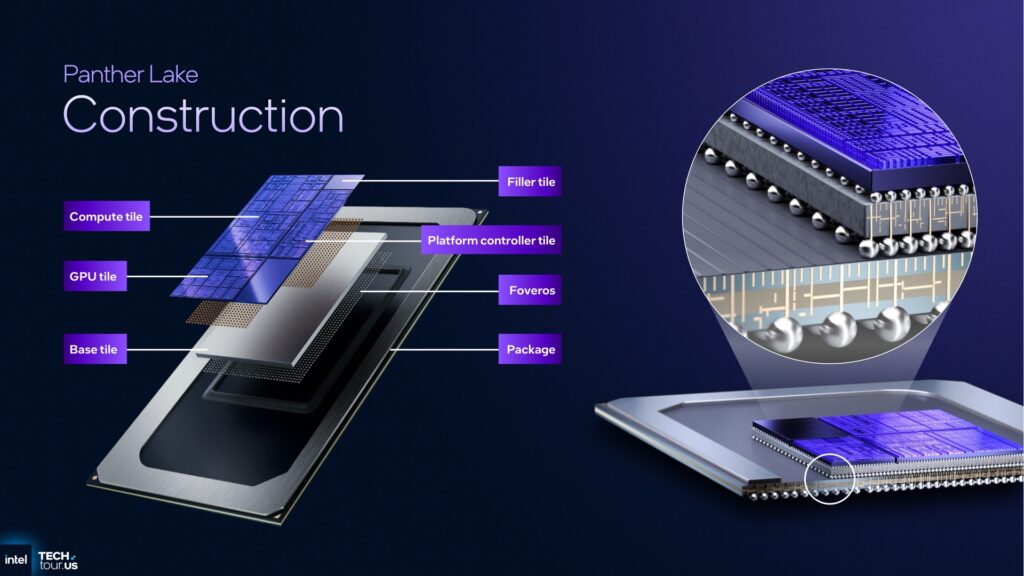
Panther Lake combines three functional chiplets using Intel’s Foveros packaging technology.
Intel
Panther Lake combines three functional chiplets using Intel’s Foveros packaging technology.
Intel
The three Panther Lake dies use the same package design, making for easy interchangeability for PC manufacturers.
Intel
Intel’s first Core Ultra chips, codenamed Meteor Lake, were introduced two years ago. There were three big changes that separated these from the 14th-generation Core CPUs and their predecessors: They were constructed of multiple silicon tiles, fused together into one with Intel’s Foveros packaging technologies; some of those tiles were manufactured by TSMC rather than Intel; and they added a neural processing unit (NPU) that could be used for on-device machine learning and generative AI applications.
The second-generation Core Ultra chips continued to do all three of those things, but Intel pursued an odd bifurcated strategy that gave different Core Ultra 200-series processors significantly different capabilities.
The most interesting models, codenamed Lunar Lake (aka Core Ultra 200V), integrated the system RAM on the CPU package, which improved performance and power consumption while making them more expensive to buy and complicated to manufacture. These chips included Intel’s most up-to-date Arc GPU architecture, codenamed Battlemage, plus an NPU that met the performance requirements for Microsoft’s Copilot+ PC initiative.
But Core Ultra 200V chips were mostly used in high-end thin-and-light laptops. Lower-cost and higher-performance laptops got the other kind of Core Ultra 200 chip, codenamed Arrow Lake, which was a mishmash of old and new. The CPU cores used the same architecture as Lunar Lake, and there were usually more of them. But the GPU architecture was older and slower, and the NPU didn’t meet the requirements for Copilot+. If Lunar Lake was all-new, Arrow Lake was mostly an updated CPU design fused to a tweaked version of the original Meteor Lake design (confused by all these lakes yet? Welcome to my world).
Source link

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ar-lays-big-change-ar-lays-2x1-39edad795d7a47f4b2ceea99834382d6.jpg)

