Getty Images Artificial intelligence has invented two new potential antibiotics that could kill drug-resistant gonorrhoea and MRSA, researchers have revealed. The drugs were designed atom-by-atom by the AI and killed the superbugs in laboratory and animal tests. The two compounds still need years of refinement and clinical trials before they could be prescribed. But the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) …
Read More »Science
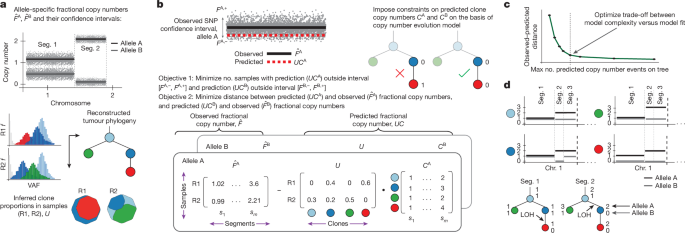
Clone copy number diversity is linked to survival in lung cancer
The ALPACA algorithm We introduce ALPACA, an algorithm to infer allele-specific copy-number profiles of every tumour clone, given three inputs that can be inferred by existing methods: estimates of allele-specific fractional copy number from multiple bulk tumour samples; a fixed number of clones and the proportion of each clone in each tumour sample; and a fixed topology of the tumour …
Read More »Just a moment…
Just a moment… Enable JavaScript and cookies to continue This request seems a bit unusual, so we need to confirm that you’re human. Please press and hold the button until it turns completely green. Thank you for your cooperation! Press and Hold Press and hold the button If you believe this is an error, please contact our support team. 209.74.74.26 …
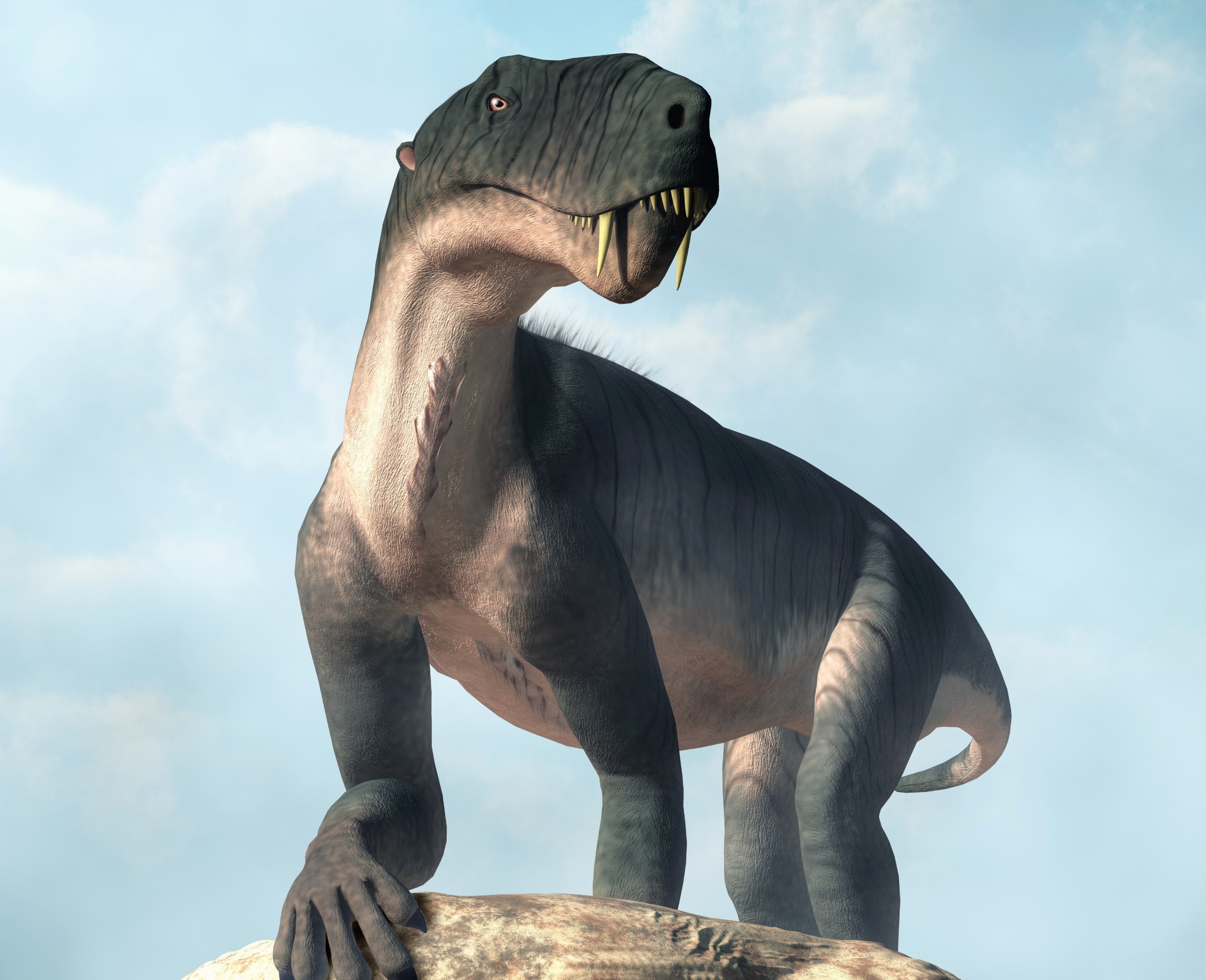
Read More »Fossils reveal thriving life before Earth’s greatest mass extinction
After years of digging across Africa, scientists have built a clearer picture of life just before Earth’s worst die-off. New fossils reveal bustling ecosystems in southern Pangea, from burrowers to tusked plant-eaters to saber-toothed hunters. The fossils show which species thrived before the “Great Dying” and hint at why so many vanished. A team led by researchers at the University …
Read More »“Superhard” Hexagonal Diamonds Found In Meteorites Produced In Bulk For The First Time
Chinese and American scientists claim to be the first to make large enough quantities of diamonds with a hexagonal structure to test their physical properties. The substance has been sought for 60 years, reflecting the extraordinary anticipated hardness of the gemstones. The team responsible may have scooped another team who described a method for achieving the same thing earlier this …
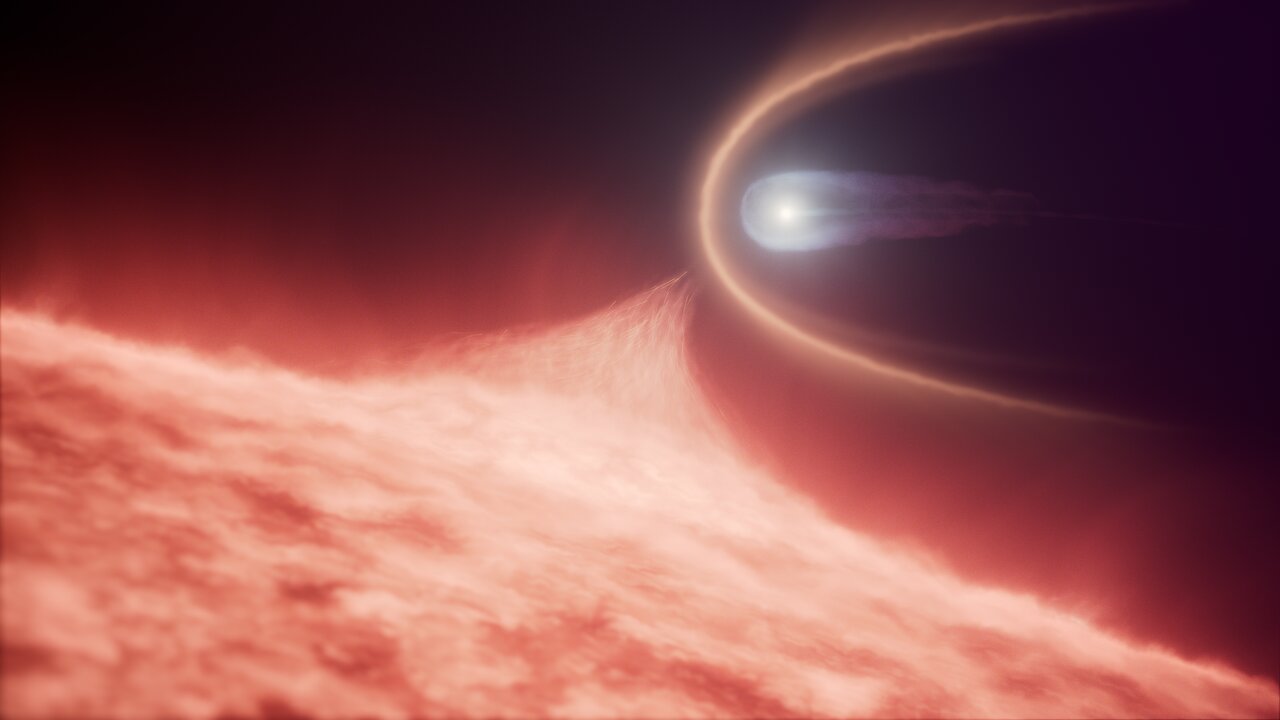
Read More »Hubble uncovers rare white dwarf merger remnant
heic2510 — Science Release 13 August 2025 An international team of astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have discovered a stellar rarity: an ultra-massive white dwarf that formed when a white dwarf merged with another star, rather than through the evolution of a single star. This discovery, which was made possible by Hubble’s sensitive ultraviolet observations, suggests that these …
Read More »Massive Hydrothermal System Discovered Beneath the Pacific Ocean
In a groundbreaking study, scientists from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) have uncovered a massive hydrogen-producing hydrothermal system beneath the western Pacific seafloor. This discovery, published in Science Advances on August 8, 2025, provides new insight into a rare and powerful process occurring far beneath the Earth’s surface. The study sheds light on the …
Read More »World-First Study Finds Surprisingly Common Mismatch Between Wild Australian Birds’ Sexual Characteristics And Genetics
A study of five common Australian bird species in southeast Queensland has found on average, 4.8 percent of them have sexual organs that don’t align with their chromosomes. The authors don’t know the cause of the deviation from biology textbooks, nor how representative the findings are for avian populations elsewhere, but it does appear to be more common than thought …
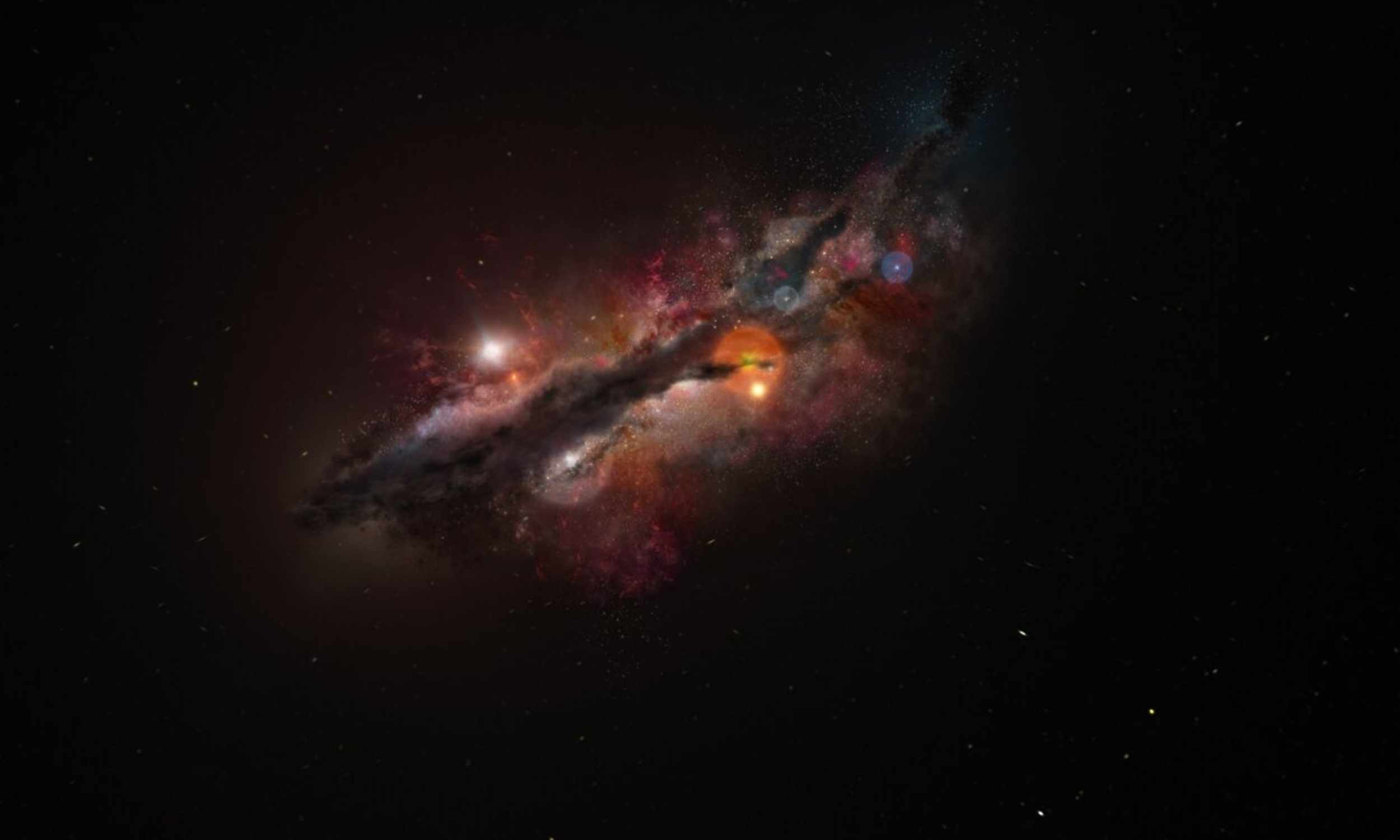
Read More »Oxygen is detected in the most distant galaxy found to date
Astronomers report that the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) has discovered traces of oxygen in the very distant and very old galaxy JADES-GS-z14-0. The light from this galaxy had traveled 13.4 billion years to reach Earth. Light from this system set out when the universe was younger than 300 million years, an era previously thought too early for heavy elements …
Read More »Tiny chip could unlock gamma ray lasers, cure cancer, and explore the multiverse
A University of Colorado Denver engineer is on the cusp of giving scientists a new tool that can help them turn sci-fi into reality. Imagine a safe gamma ray laser that could eradicate cancer cells without damaging healthy tissue. Or a tool that could help determine if Stephen Hawking’s multiverse theory is real by revealing the fabric underlying the universe. …
Read More »