| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
In the vast expanse of our universe, few celestial bodies have captured the fascination and intrigue of scientists and stargazers alike as much as Betelgeuse. Known for its shimmering brightness visible to the naked eye, this red supergiant star, located in the Orion constellation, has been a subject of intense study and curiosity for centuries. Recent astronomical observations have finally uncovered a groundbreaking revelation—the existence of a long-speculated companion star. This discovery not only solves a long-standing mystery but also sheds light on the dynamic and evolving nature of Betelgeuse, promising to redefine our understanding of stellar systems.
The Discovery of Betelgeuse’s Elusive Companion
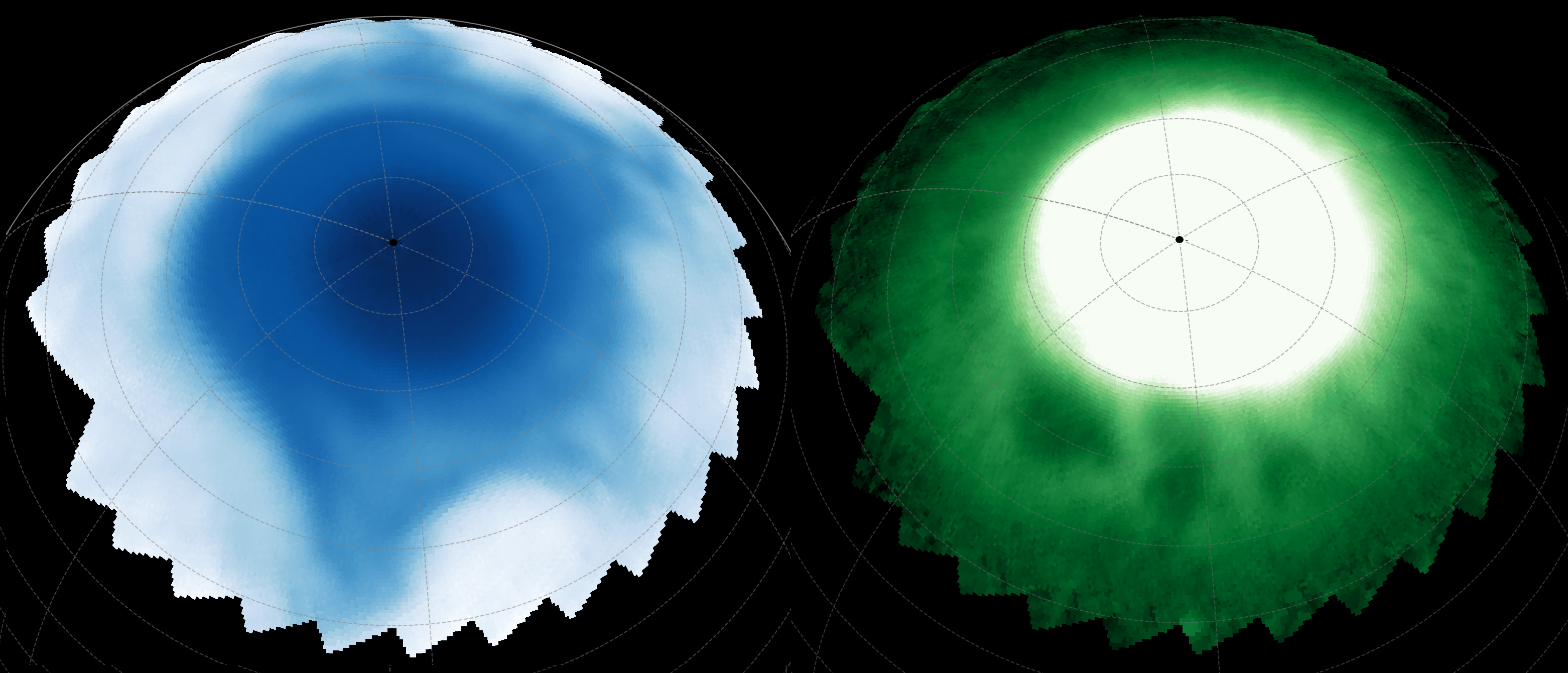
For decades, astronomers have speculated about the presence of a hidden companion star orbiting Betelgeuse. The fluctuating brightness of Betelgeuse, especially its six-year dimming cycle, hinted at the gravitational influence of another celestial body. Using the advanced ‘Alopeke instrument on the Gemini North telescope, scientists have finally confirmed the existence of this elusive companion. The ‘Alopeke instrument, which employs a technique known as speckle imaging, has enabled researchers to obtain high-resolution images, effectively piercing through the distortions caused by Earth’s atmosphere.
This marks the first time a companion star has been directly detected so close to a red supergiant, offering astronomers a unique opportunity to study the dynamics within such binary systems. The discovery was led by Steve Howell from NASA Ames Research Center, whose team’s perseverance paid off, overcoming previous technological limitations that had hindered such direct observations.
Understanding the Characteristics of the Companion Star
Betelgeuse’s companion star is estimated to have a mass about 1.5 times that of our sun. It is a hot blue-white star, orbiting at a distance approximately four times the separation between Earth and the sun. This relatively close proximity means it resides within the extended atmosphere of Betelgeuse, a fact that has significant implications for both stars.
Interestingly, while Betelgeuse is nearing the end of its life, its companion is still in its early stages, not yet having initiated hydrogen fusion in its core. This juxtaposition highlights the diversity in stellar evolution, even among stars that form simultaneously. Despite its youth, the companion’s fate is intertwined with Betelgeuse’s, as the gravitational pull of the massive red supergiant is expected to eventually draw it in, leading to a dramatic merger in the distant future.
The Implications of the Great Dimming
The dramatic “Great Dimming” event that occurred between 2019 and 2020 sparked global interest and speculation about Betelgeuse’s imminent supernova. Though initially thought to signal an impending explosion, further research revealed that this dimming was caused by a vast cloud of dust. This finding has calmed fears of Betelgeuse’s immediate demise but has also intensified scientific interest in its regular six-year dimming cycle.
This periodic dimming, now attributed to the newly discovered companion star, adds another layer to our understanding of Betelgeuse’s complex behavior. It also underscores the importance of continuous observation and study, as each discovery builds upon the last, gradually unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos.
The Future of Observations and Research
The detection of Betelgeuse’s companion has opened new avenues for astronomical research. As the first of its kind, this observation pushes the boundaries of what can be achieved with current technology, setting a precedent for future studies of similar stellar systems. The team plans to observe the companion again in November 2027, when it will be at maximum separation from Betelgeuse, providing further insights into their interaction.
This discovery not only enhances our understanding of Betelgeuse but also contributes to the broader field of stellar evolution. By studying these giant celestial bodies, scientists can better comprehend the processes that govern the life cycles of stars, contributing to our overall knowledge of the universe. As we look to the future, the question remains: what other secrets do the stars hold, waiting to be uncovered by the next generation of astronomers?
The revelation of Betelgeuse’s companion star marks a significant milestone in astronomy, offering fresh perspectives on stellar dynamics and evolution. As we continue to explore the cosmos, each discovery brings us closer to understanding the intricate tapestry of our universe. With new technologies and ever-growing curiosity, we must ask ourselves: what mysteries lie beyond, waiting to be discovered in the silent expanse of space?
This article is based on verified sources and supported by editorial technologies.
Did you like it? 4.4/5 (25)
Source link